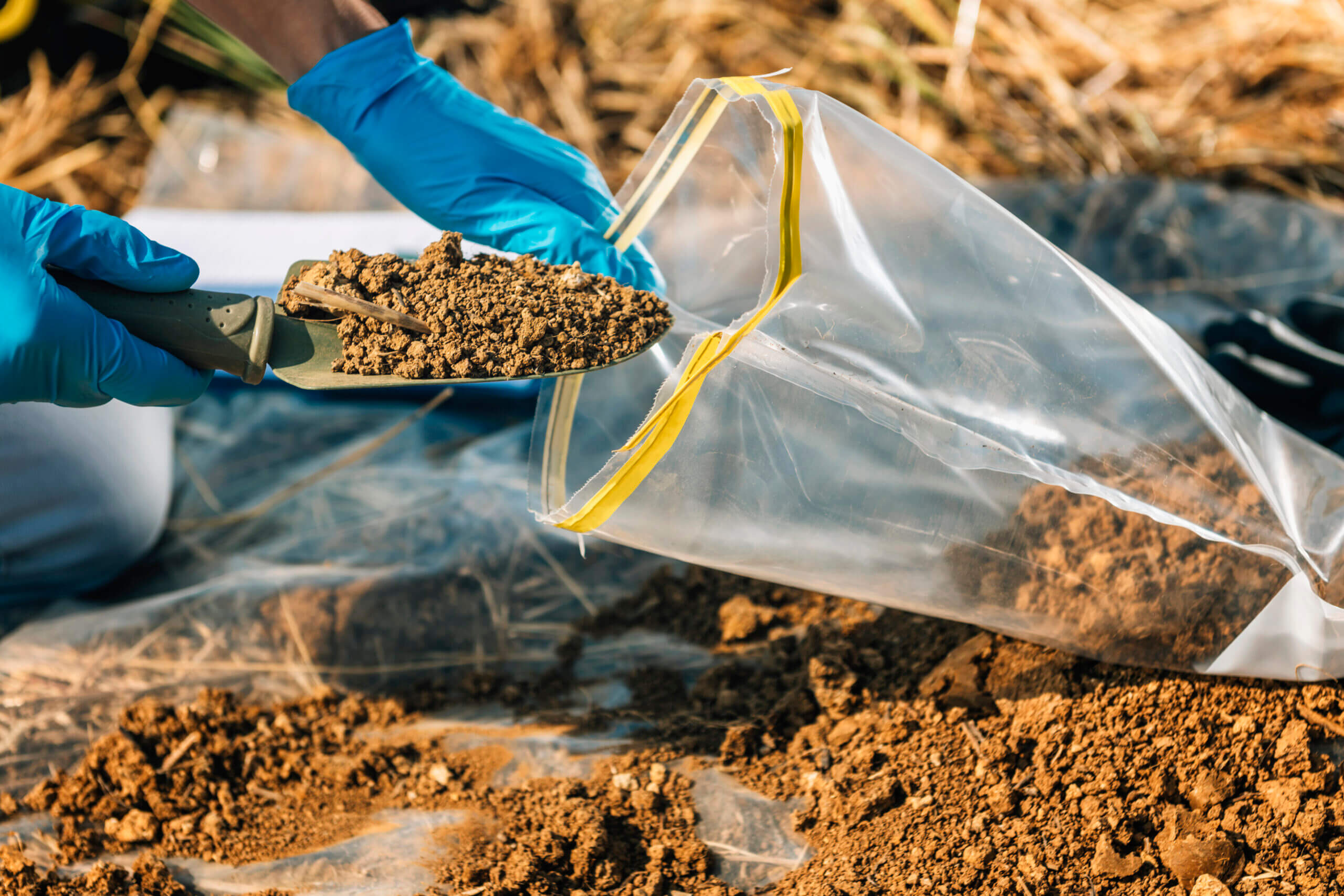
A strong foundation is the backbone of any successful construction project. Whether it's a residential building, commercial property, or infrastructure project, the stability and longevity of the structure rely heavily on the quality of the ground beneath it. Soil testing plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of the soil and ensuring a robust foundation that can withstand loads and environmental conditions for years to come.
What Is Soil Testing?
Soil testing involves analyzing the physical and chemical properties of the soil on a construction site. It includes various tests to assess the soil's strength, density, moisture content, compaction, and load-bearing capacity. These insights provide engineers and builders with the necessary data to design safe and efficient foundations that match the ground conditions.
Why Is Soil Testing Important?
- Understanding Soil Strength and Stability: Soil testing helps determine the strength and stability of the ground. Tests such as California Bearing Ratio (CBR), Plate Load Testing, and Triaxial Testing reveal the soil's ability to support the structure's weight. Weak or loose soils can cause foundation failure if not addressed.
- Choosing the Right Foundation Type: Different soil types require different foundation systems. For instance, strong, dense soils may allow for shallow foundations, while soft or expansive soils might require deep foundations like piles or piers. Soil testing provides clarity to select the most suitable foundation type.
- Mitigating Risk and Reducing Costs: Conducting soil tests upfront helps identify and resolve potential problems before construction begins. This proactive approach saves significant time, money, and resources by minimizing delays, rework, or structural damage in the future.
- Ensuring Compliance: Soil testing is often required to meet building codes, safety regulations, and environmental standards. It ensures the project adheres to legal and engineering guidelines.
Key Soil Testing Methods
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT): Determines soil density and resistance.
- Atterberg Limits Test: Measures soil consistency and plasticity.
- Moisture Content Test: Assesses the water content of the soil.
- Bearing Capacity Test: Evaluates the soil's load-bearing capacity.
These tests provide essential data to help engineers design a foundation that is strong, durable, and resistant to environmental changes.
The Role of Soil Testing in Preventing Failures
Poor soil conditions can lead to foundation cracks, uneven settling, or complete structural failure. Notable examples include buildings constructed without proper soil assessment that experience long-term damage or collapse. With accurate soil testing, builders can identify potential risks and implement corrective measures, ensuring a safe and stable structure.
Soil testing is a fundamental step in any construction project. It provides critical information about the soil's strength, composition, and behavior, enabling engineers to design foundations that support the structure safely and efficiently. By investing in professional soil testing services, builders can minimize risks, avoid costly repairs, and guarantee a solid foundation that stands the test of time. For reliable soil testing and geotechnical consulting services, contact our team today to ensure your project begins with confidence and stability.